 Lviv Radio Engineering Research
Institute (LRERI), Ukraine
Lviv Radio Engineering Research
Institute (LRERI), Ukraine Lviv Radio Engineering Research
Institute (LRERI), Ukraine
Lviv Radio Engineering Research
Institute (LRERI), Ukraine|
|
LRERI provides to the world market subjects a broad range of R&D services into radar technologies and command and control systems.
Our core activities centre around millimeter radar technology and armoured vehicle based command and control systems.
Typically our method is to prototype hardware. We have been working hard to move technology out of the Institute to marketplace.
LRERI offers to potential customers fee based services on carrying out R&D relating to millimeter wave radar technology, including all weather, day and night radar sights, search and fire control radars (SFCR), short-range air defense radars (SRADR) and armoured vehicles based command and control systems (AVCCS) including armoured vehicle movement control subsystems (AVMCS), command and control facilities for fire control subsystems (CCFFCS), navigation subsystem (NS), laser weapon defense subsystem (LADS) in accordance with the performance specifications presented by the customers.
A. Surveillance Artillery Sighting Radar (SASR) with (85 - 100) GHz range
B. Armoured Vehicles based Command and Control Systems (AVCCS)
- Search and Fire Control Radar (SFCR)
- Command and Control Facilities for Fire Control Subsystem (CCFFCS)
- Armoured Vehicle Movement Control Subsystem (AVMCS)
- Navigation Subsystem (NS)
- Laser Weapon Defense Subsystem (LWDS)
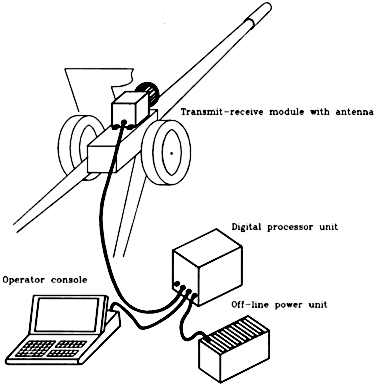
LRERI proposes to develop solid-state SASR with (85-100 GHz) range for detection the equipment, their highly accurate tracking, precision coordinate measurement and guidance of barrel armament with no optical visibility.
- coherent-pulse sequence of probing signals with pulse-to-pulse carrier frequency jumping;
- coherent processing using multiple point FFT;
- distributed (multiprocessor) system for processing target return signal in information channels of the Radar and the control of its operation modes.
- azimuth coverage .............................. sectoral ±6 degrees of arc;
- angular altitude coverage ................. sectoral ±6 degrees of arc;
- detection rang:
mobile tank ................................. 3-5 km;
fixed tank .................................... 1.5 km;
- tracking error:
azimuth ...................................... not more than 1 angular minute;
range .......................................... not more than 5.0 m;
radial velocity ........................... not more than 1 m/s;
- resolution:
azimuth ..................................... not more than 30 angular seconds;
range ......................................... not more than 10 m;
radial velocity .......................... not more than 1 m/s;
- weight ............................................... 50 kg;
- volume ............................................... 0.07 cub.m.
LRERI proposes to develop AVCCS for new main battle tanks and armoured fighting vehicles upgrades. The computerized AVCCS assists MBT commanders to make faster, better and more informed decisions based on all relevant data from battlefield system, thermal, optic imagers and TV-cameras and AVCCS major subsystems such as Navigation Subsystem, Fire Control Subsystem, Armoured Vehicle Movement Control Subsystem, Laser Weapon Defense Subsystem.
LRERI proposes to develop 3 millimeter wave band SFCR for main battle tanks applications. SFCR can be customized for various weapon systems and integrated into Vehicle Command and Control System as a part of Vehicle Fire Control Subsystems.
Range ......................................................................... 5 km
Coordinate accuracy (mean-root-square error)
- azimuth, elevation angle .................................... 1 angular minute
- range.................................................................. 5 m
- radial velocity................................................... 1 m/s
Resolution:
- range.................................................................. 0.5 - 10 m
- radial velocity................................................... 0.5 m/s
Observation zone dimensions (programm-based):
- azimuth ............................................................. 30 degrees
- elevation .......................................................... 20 degrees
Target indication:
- visual
- audial
Operating characteristics:
- automatic equipment testing
- electric alignment
- IBM computer interface capability by a shared channel
- target classification
- circuit power consumption 27V, not more than 1.2kW
- operating temperature range .............................. -50œ ÷ +50 deg. cent.
Equipment complete set:
- radio unit............................................................ 40 cub. dm
- digital processing unit........................................ 60 cub. dm
- control console..................................................... 3 cub. dm
- data presentation unit........................................ 7.5 cub. dm
LRERI proposes to develop CCFFCS for new MBT and armoured vehicles upgrades. These facilities are utilized for ballistic computation and normalization of stabilizer signals proportional to gun lead and elevation angles.
CCFFCS comprise: display and parameter input consoles, ballistic computer unit and use input information provided by signals from:
1) sights:
- range
- guidance angles
2) atmosphere parameter sensors:
- air temperature
- air pressure
- wind strength and direction
3) sensors:
- turret position
- gun position
- roll, pitch
- ballistic type
4) projectile firing speed instrument (muzzle velocity system):
- initial projectile speed.
LRERI proposes to develop AVMCS in order to enhance vehicle mobility parameters using computerized control of basic and auxiliary engines and a gear-box.
The subsystem includes: driver’s display consoles, basic engine and gear-box control unit, auxiliary engine control unit, reversing gear control unit, movement sensors.
AVMCS provides:
- test and display of basic and auxiliary engine parameters
- computerized start and stop of basic and auxiliary engines
- optimal fuel feed by computing the position of a control rack based on combined real road and engine parameters
- computerized gear shift from downshift to upshift and vice versa
- maintaining of auxiliary engine speed as dependent on the load
- reversing gear control
- duplicated control mode
LRERI proposes to develop NS for all types of armoured vehicles that can be applied for the purposes as set forth:
- measurement of current coordinates of terrain, road speed and time by SNS GLONASS and GPS NAVSTAR radio signals in any place of the Globe, at any time and under any weather conditions
- destination assignment for the commander himself and the personnel under his command (by using the radio link), measurement of the distance to this point of destination, deflection angle and time of arrival according to the operator's instructions
- subordinate location polling
- telecode reception-transmission
- storage of 50 route placesNS consists of: commander's console, operator's console, control unit, navigator receiver, movement sensors, radio station.
30 m |
|
| GPS coordinates | 40 m |
| GLONASS/ GPS coordinates | 20 m |
| Speed | 0.1m/s |
| Time of readiness after starting | 5 min |
LRERI proposes to develop LWDS for all types of armoured vehicles. LWDS
is intended to decrease vulnerability to weapons utilizing laser illumination
in operation.
The subsystem warns the crew that the vehicle is illuminated by a laser
range finder or a laser target designator, provides automatic turn of
turret for firing countermeasures and aerosol screening taking into account
illumination, its own movement and wind directions.
LWDS incorporates: console, analyzer and control unit, nuclear illumination
analyzers, aerosol grenades, IR headlights.
Analyzer spectral range ............................................................................ 0.6 to 12 mu;
Overall horizon field of view ................................................................... 360 degrees;
Minimum analyzer resolution in most vulnerable directions .................... 3.75 degrees;
Quantity of aerosol grenades .................................................................... 12 pcs;
Light and sound warning capability.